Google Analytics filters are powerful tools that allow users to monitor website traffic more accurately, segment data more effectively and gain valuable insights into their visitors’ behaviour. Using filters, users can filter out irrelevant data, customize reports, track specific campaigns or keywords and glean deeper insights into their website performance.
If you’re a small business or digital marketer that wants to get the most meaningful information out of your Google Analytics data, then look no further than filters. Filters are essential for gaining insight into customer behavior, understanding how successful your campaigns are performing, and getting an accurate account of website traffic and activity.
To take full advantage of all the metrics and insights available in Google Analytics, it’s important to understand how filters work and what best practices should be employed when creating them. In this guide we’ll give you a comprehensive overview on the different types of Google Analytics Filters available, explain when each type is useful, provide step by step instructions for setting up filters within your analytics accounts, and share some expert tips from leading professionals in the industry.
No matter what level of experience you have with analytics tools or if this is entirely new territory for you, after reading through this article you will come away confidently equipped to start using filers like a pro!
For instance, a user could apply a filter to exclude all visits from a certain IP address or geographical area. Or they could use it to create a report containing only organic traffic from a particular country. They could also set up goal tracking and roll-up reporting using filters to get the most out of their Google Analytics account.
The possibilities are virtually limitless – users just have to be creative with how they apply filters and make sure that each one serves an important purpose in helping them gain insights into their visitor behaviour. So if you’re looking for ways to take your website analytics game to the next level, setting up appropriate Google Analytics Filters is definitely something you should consider!
Overview of Google Analytics Filters – What They Are and How to Use Them
Google Analytics is a powerful tool for tracking and analyzing website traffic. However, with so much data available, it can be overwhelming to sift through it all. That’s where filters come in. They allow you to refine your data and focus on specific subsets that are most relevant to your business goals. For example, you can use filters to exclude internal traffic from your office, or to track only mobile visitors. In this article, we’ll explore what filters are and how to use them effectively in your Google Analytics account. So if you’re looking to take your data analysis to the next level, read on!
Types of Filters Available in Google Analytics
As any seasoned marketer knows, Google Analytics is a goldmine of data that can be used to optimize website performance and make informed business decisions. One of the key features of this platform is the ability to set up various filters to modify and segment your data. From excluding internal traffic to filtering pages based on specific parameters, there are a wide variety of filters available to help you get the most out of your Google Analytics account.
However, with so many different types to choose from, it can be difficult to decide which filters to apply and when. In this paragraph, we will explore some of the most common types of filters available in Google Analytics and how they can be used to improve your data analysis.
Google Analytics filters allow you to customize the data that is sent from your website and applications tracked with Google Analytics. Filters are the best way to modify and control the data you collect in reports, allowing only certain requests to be processed by Google Analytics.
There are different types of filters available in Google Analytics: include filters, exclude filters, search & replace filters, and advanced (custom) filters. Let’s look at each filter type and some examples of each:
Predefined Filters
Predefined Filters: Google Analytics provides several predefined filters that you can use to exclude or include specific types of traffic. For example, you can use the “Exclude Internal Traffic” filter to exclude traffic from your organization’s IP address, or the “Exclude Known Bots and Spiders” filter to exclude traffic from known bot and spider user agents.
Custom Filters
Custom Filters: You can also create custom filters to include or exclude specific types of traffic based on custom criteria that you define. For example, you can use a custom filter to include traffic only from a specific subdomain or directory on your website, or to exclude traffic from a specific country or region.
Advanced Filters
Advanced Filters: Advanced filters are more complex filters that allow you to combine multiple filter conditions to create more specific and granular filters. For example, you can use an advanced filter to exclude traffic from a specific subdomain and only include traffic from a specific country.
Include Filters
Include Filters- Include Filters help you refine what data gets included in your report analysis by including or excluding data based on certain criteria. For example: You can apply an include filter so that only traffic from a specific country will get counted or only traffic coming from organic sources like search engine results will be shown in your report.
Exclude Filters
Exclude Filters- Exclude Filters let you make sure that any specified information is not used for reporting purposes. For example: You can use an exclude filter if there is a specific IP address that keeps showing up as site visits; this excludes it from being counted towards your overall visit totals but still shows up for individual user tracking purposes instead of showing up in aggregated reports like general location information does.
Search and Replace Filters
Search & Replace Filters- Search & Replace lets users adjust values within field names before they show up in reports such as cleaning up URLs when one page has multiple URL formats due to different parameters such as UTM codes added on through links etc. Search and replace filters allow you to search for specific patterns in your data and replace them with other values. For example, you can use a search and replace filter to replace a misspelled or inconsistent campaign parameter with a corrected value.
Setting up views with filters
Here are step-by-step instructions on how to set up views with filters in Google Analytics:
- Create a New View: The first step in setting up a view with filters is to create a new view. To do this, log in to your Google Analytics account and click on the “Admin” button in the bottom left-hand corner of the screen. Then, click on “Create View” and follow the prompts to enter a name for the view and select the relevant time zone and currency.
- Set up Filters: After creating the new view, click on the “Filters” tab to set up filters. Click on “Add Filter” and follow the prompts to create a new filter. There are several types of filters you can create, including exclude, include, search and replace, and lowercase/uppercase. Choose the appropriate filter type and define the specific criteria you want to exclude or include.
- Apply the Filters: Once you have set up your filters, you need to apply them to your view. To do this, click on the “View Settings” tab and scroll down to the “Filters” section. Check the box next to each filter you want to apply to the view.
- Verify the Filters: After applying the filters, you need to verify that they are working correctly. To do this, navigate to the “Reporting” tab and select the new view you created from the dropdown menu at the top of the screen. Then, navigate to the report that corresponds to the filter you set up and check that the data is being filtered correctly.
- Create Multiple Views: You can create multiple views with different filters to get a more comprehensive view of your website traffic and user behavior. For example, you might create one view with filters that exclude internal traffic, and another view that only includes traffic from a specific geographic location.
- Modify or Remove Filters: If you need to modify or remove filters, simply navigate back to the “Filters” tab in the “Admin” section and make the necessary changes.
By setting up views with filters in Google Analytics, you can gain more targeted insights into your website traffic and user behavior, and make more informed decisions about your online presence.
How to Create a Custom Filter for Your Website
When it comes to designing and maintaining a website, having the ability to control what your audience sees is key. One way to achieve this is by creating custom filters that allow you to decide which content is displayed to your visitors. Whether it’s hiding specific posts or images, or filtering out spam comments, custom filters give you the power to curate your website’s content to your liking.
However, creating a custom filter can be intimidating, especially if you’re not familiar with coding. But fear not, with a little guidance, you can easily create a custom filter that fits your website’s unique needs. In this article, we’ll explore the ins and outs of creating a custom filter and how it can take your website to the next level.
Here are the step-by-step instructions for creating a custom filter in Google Analytics:
- Step 1: Log in to Google Analytics and select the website you want to create a filter for.
- Step 2: In the left-hand navigation menu, click on the “Admin” button. This will take you to the Admin panel.
- Step 3: In the “View” column, click on the “Filters” option. Then, click on the “+ Add Filter” button.
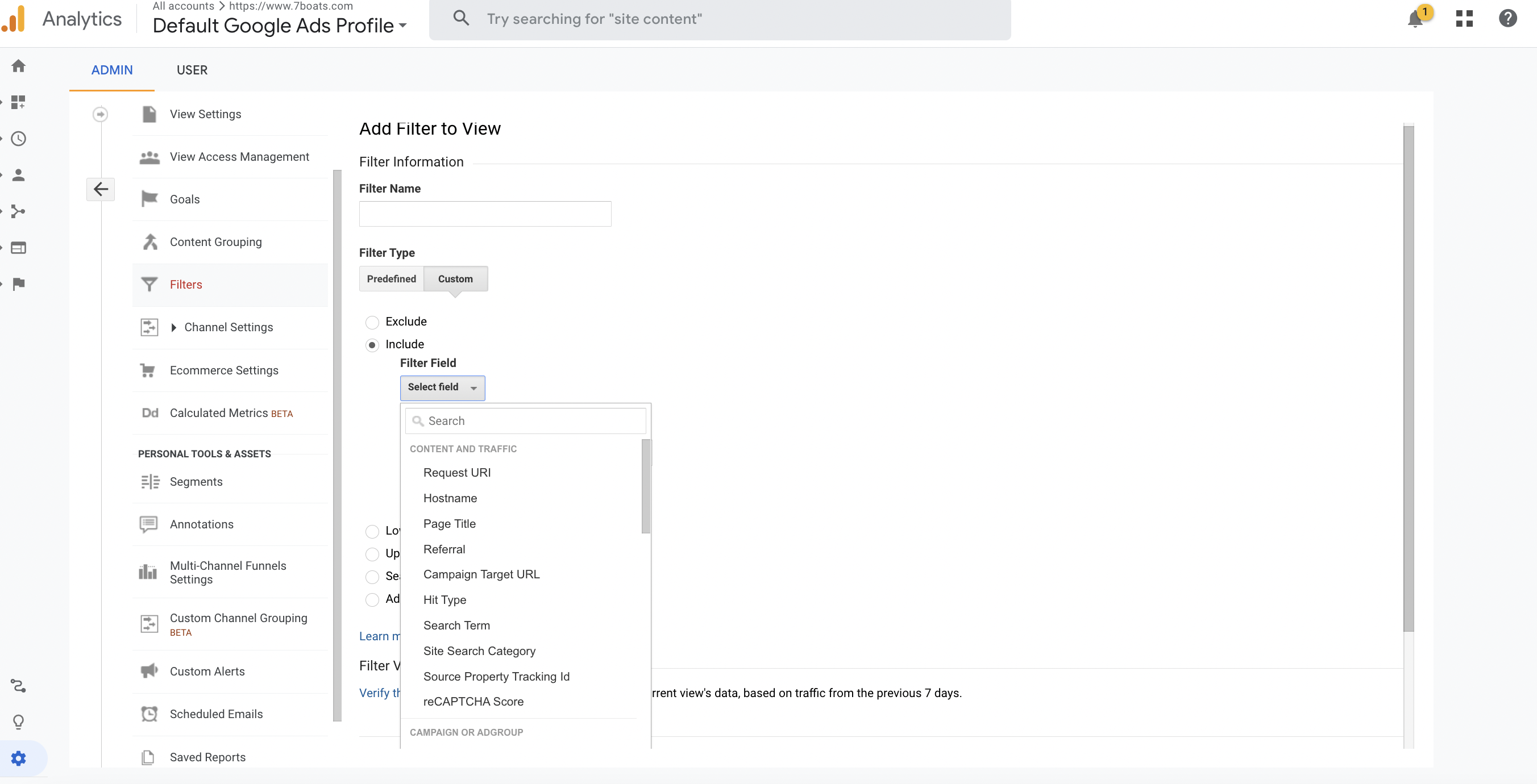
- Step 4: On the “Add Filter to View” screen, enter a name for your filter in the “Filter Name” field.
- Step 5: Select the filter type you want to create. Google Analytics offers several filter types, including predefined filters and custom filters. For this example, we will create a custom filter.
- Step 6: Select the filter field you want to use. This will depend on the data you want to filter. In this example, we will use the “Request URI” filter field to exclude specific pages from our data.
- Step 7: Choose the filter pattern you want to use. This will depend on the specific pages you want to exclude. For example, if you want to exclude all pages that contain “test” in the URL, you would enter “test” as the filter pattern.
- Step 8: Choose the filter action. In this example, we want to exclude the specified pages, so we will select the “Exclude” filter action.
- Step 9: Preview your filter to make sure it is working correctly. You can use the “Verify this filter” button to test your filter against your data.
- Step 10: Once you are satisfied with your filter, click on the “Save” button to apply it to your data.
That’s it! Your custom filter is now applied to your Google Analytics data. Keep in mind that it may take some time for your filtered data to start showing up in your reports. It’s also important to regularly review and update your filters to ensure they are still relevant and necessary for your analysis needs.
Common RegEx expressions to use in Google analytics Filters
Here are some common RegEx expressions that can be used in filters in Google Analytics:
- ^/blog/ – This will match any page that starts with “/blog/” in the URL.
- /contact-us$ – This will match the exact URL “/contact-us”.
- \d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2} – This will match any date in the format “yyyy-mm-dd”.
- (google|bing|yahoo) – This will match any traffic that comes from Google, Bing, or Yahoo.
- .(jpg|gif|png)$ – This will match any URL that ends with “.jpg”, “.gif”, or “.png”.
- ^(?!/admin/).*$ – This will match any URL that does not start with “/admin/”.
- [A-Z]{2}-\d{3,4}-\d{2,3} – This will match any format of a specific pattern, such as a license plate number.
- \b[A-Z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Z0-9.-]+.[A-Z]{2,}\b – This will match any valid email address.
These RegEx expressions can be used in various filter types, such as Include Filters, Exclude Filters, Search and Replace Filters, and Advanced Filters. By using RegEx expressions in filters, you can create more complex and precise filters that can help you analyze your data more effectively.
Some examples of custom filters in Google Analytics using RegEx
Here are some examples of custom filters in Google Analytics using RegEx:
- Filter to exclude internal traffic: This filter can be used to exclude traffic from internal sources, such as your company’s IP address. You can create a custom filter with the following settings:
- Filter Name: Exclude Internal Traffic
- Filter Type: Predefined
- Select Filter: Exclude traffic from the IP addresses that are equal to
- IP Address: Enter the IP address of your company’s network
- Apply Filter to Views: Select the views that you want to apply the filter to
- Filter to include only specific directories: This filter can be used to include only certain directories or folders in your reports. You can create a custom filter with the following settings:
- Filter Name: Include Specific Directories
- Filter Type: Custom
- Filter Field: Request URI
- Filter Pattern: ^/(directory1|directory2)/
- Filter Type: Include
- Apply Filter to Views: Select the views that you want to apply the filter to
- Filter to exclude specific pages: This filter can be used to exclude specific pages from your reports. You can create a custom filter with the following settings:
- Filter Name: Exclude Specific Pages
- Filter Type: Custom
- Filter Field: Request URI
- Filter Pattern: /(page1|page2|page3)/
- Filter Type: Exclude
- Apply Filter to Views: Select the views that you want to apply the filter to
- Filter to convert URLs to lowercase: This filter can be used to convert all URLs to lowercase, which can help prevent duplication of data in your reports. You can create a custom filter with the following settings:
- Filter Name: Convert URLs to Lowercase
- Filter Type: Custom
- Filter Field: Request URI
- Filter Pattern: (.*)
- Filter Type: Lowercase
- Apply Filter to Views: Select the views that you want to apply the filter to
- Filter to include only traffic from a specific subdomain: This filter can be used to include only traffic from a specific subdomain of your website. You can create a custom filter with the following settings:
- Filter Name: Include Subdomain Traffic
- Filter Type: Custom
- Filter Field: Hostname
- Filter Pattern: subdomain.example.com
- Filter Type: Include
- Apply Filter to Views: Select the views that you want to apply the filter to
- Filter to exclude referral spam: This filter can be used to exclude referral spam from your reports. You can create a custom filter with the following settings:
- Filter Name: Exclude Referral Spam
- Filter Type: Custom
- Filter Field: Campaign Source
- Filter Pattern: (spam1|spam2|spam3)
- Filter Type: Exclude
- Apply Filter to Views: Select the views that you want to apply the filter to
- Filter to include only traffic from a specific country: This filter can be used to include only traffic from a specific country. You can create a custom filter with the following settings:
- Filter Name: Include Country Traffic
- Filter Type: Custom
- Filter Field: Country
- Filter Pattern: country name or ISO code
- Filter Type: Include
- Apply Filter to Views: Select the views that you want to apply the filter to
- Filter to exclude parameters from URLs: This filter can be used to exclude parameters from URLs, which can help prevent duplication of data in your reports. You can create a custom filter with the following settings:
- Filter Name: Exclude URL Parameters
- Filter Type: Custom
- Filter Field: Request URI
- Filter Pattern: (.)(?|&)(utm_source|utm_medium|utm_campaign)(=[^&])(.*)
- Output To: Request URI
- Apply Filter to Views: Select the views that you want to apply the filter to
9. Exclude Dev Site Traffic
To exclude development and staging traffic data from your production view, a.k.a. Main View, create the following filter:
- Filter Name: Exclude Dev Site Traffic
- Filter Type: Custom > Exclude
- Filter Field: Hostname
- Filter Pattern: Enter a regex pattern of all development hostnames for your website. For example, if the development hostnames are dev.example.com, backend.example.com, and stage.example.com you would enter ^dev\.example\.com$|^backend\.example\.com$|^stage\.example\.com$ in this field (or some similar Regex).
10. Remove Query String
Sometimes, you may want a view that removes all query strings from your page URLs. You can accomplish this with an advanced filter.
- Filter Name: Remove Query String
- Filter Type: Custom > Advanced
- Field A -> Extract A:
- Select Request URI
- Enter ^([^?]+)
- Output To -> Constructor:
- Select Request URI
- Enter $A1
- Select Field A Required
- Select Override Output Field
These are just a few more examples of custom filters that can be created in Google Analytics using RegEx. By using RegEx expressions in filters, you can create more advanced and precise filters to help you analyze your data more effectively.
How to Apply Multiple Filters in Google Analytics?
To apply multiple filters in Google Analytics, you can create a filter sequence. A filter sequence is a series of filters that are applied to your data in a specific order. This allows you to apply multiple filters to your data, and to control the order in which they are applied.
Here’s how to apply multiple filters using a filter sequence:
- Log in to your Google Analytics account, and select the view that you want to apply the filters to.
- Click on the “Admin” tab in the top navigation bar, and then click on “Filters” under the “View” column.
- Click on the “Add Filter” button to create a new filter.
- Choose the type of filter that you want to apply, and configure the filter settings.
- Click on the “Save” button to create the filter.
- Repeat steps 3-5 to create additional filters.
- Once you have created all of the filters that you want to apply, click on the “Filter Order” tab at the top of the page.
- Drag and drop the filters into the order that you want them to be applied.
- Click on the “Save” button to save the filter sequence.
When you apply multiple filters using a filter sequence, the filters are applied in the order that you specify. This means that the first filter in the sequence is applied first, followed by the second filter, and so on. By using a filter sequence, you can apply multiple filters to your data, and control the order in which they are applied, allowing you to customize your data to meet your specific needs.
Tips for Applying Google Analytics Filters to Maximize Results
Here are some tips for applying Google Analytics filters to maximize results:
- Understand your data: Before applying filters, it’s important to understand your data and identify any specific patterns or trends that you want to track. This will help you create filters that are most effective for your needs.
- Set up a test view: It’s always a good idea to create a test view before applying filters to your main view. This allows you to test and refine your filters without affecting your main data.
- Use the right filters: There are many different filters available in Google Analytics, so it’s important to choose the right ones for your needs. Some common filters include exclude filters, include filters, search and replace filters, and lowercase filters.
- Prioritize your filters: It’s important to apply your filters in the right order. Filters are applied in the order they appear in your filter list, so prioritize the most important filters first.
- Regularly review and update filters: It’s important to regularly review and update your filters to ensure they are still relevant and necessary. This will help ensure your data remains accurate and useful.
- Use regular expressions: Regular expressions (regex) allow you to create more complex filters that can include or exclude specific patterns of data. This can be especially useful for excluding spam or bot traffic.
- Be careful with permanent changes: Applying filters can permanently change your data, so be careful when making permanent changes. Always test your filters before applying them to your main view.
- Use annotations: Annotations are a great way to keep track of changes made to your data. Use annotations to document any changes made with filters or other data manipulations.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your Google Analytics filters are effective and useful for tracking your website’s performance.
Best Practices for Managing and Analyzing Data with Filters
In today’s fast-paced world, effective data management has become a vital part of organizational success. With the ever-increasing volume of data available, it’s important to have tools and best practices in place to efficiently filter and analyze the information. Whether you’re working with customer data or financial reports, filters can help you easily sift through the noise and focus on the most relevant data.
However, it’s important to have a clear understanding of how to effectively use filters to ensure accuracy and reliability of your data analysis. By following best practices for managing and analyzing data with filters, you can gain valuable insights and make informed decisions that drive business growth.
- Define goals and objectives for using filters in Google Analytics, and ensure that these align with overall business objectives and strategies.
- Always create a copy of the original view before applying any filters to ensure data is not permanently altered.
- Use filters to exclude internal traffic, such as from your company’s IP addresses, to ensure accurate tracking of external visitors.
- Create separate views for different types of traffic, such as mobile and desktop, to allow for easy comparison and analysis.
- Utilize regular expressions (regex) to create more complex filters for specific patterns of data, such as excluding all traffic from a particular country or region.
- Use filters to include or exclude specific pages or sections of your website for more targeted analysis of user behavior.
- Test filters thoroughly before applying them to important views or data to ensure they are working as intended.
- Use annotations in Google Analytics to document any changes made with filters or other data manipulations for future reference.
- Regularly review and update filters to ensure they are still relevant and necessary for your analysis needs.
- Understand that applying filters may impact your data history, so it’s important to consider this before applying any permanent changes.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Filters in Google Analytics
Google Analytics is an essential tool for businesses of all sizes. It allows them to track their website traffic, analyze user behavior, and make informed decisions to optimize their online presence. However, sometimes filters in the tool can cause issues that prevent businesses from getting the insights they need. For instance, filters may not be set up correctly, or they may block out essential data. Troubleshooting these common issues is vital to ensure accurate and useful data in Google Analytics. Fortunately, with a little knowledge and guidance, businesses can quickly resolve these issues and get back to using Google Analytics to its fullest potential.
There are several common issues that can arise when using filters in Google Analytics. Here are some of the most common issues and potential solutions:
- Incorrectly configured filters: Ensure that your filters are properly configured and applied to the correct views. Double-check your filter settings and make sure they are not conflicting with other filters.
- Data sampling: If your data is being sampled, it may be due to the use of filters. To reduce sampling, consider using filters with less complex rules or remove them altogether.
- Incorrect data: Ensure that the filters you apply are accurately reflecting the data you want to include or exclude. Check your filters against your data and make sure they are functioning as intended.
- Missing data: Filters can sometimes exclude data that you intended to include. Check to see if any data is missing and adjust your filters accordingly.
- Inaccurate results: If you are seeing inaccurate results, check your filters to ensure they are properly configured and applied. Consider removing filters to see if this resolves the issue.
- Filter order: The order in which filters are applied can impact your results. Review the order of your filters and make sure they are applied in the correct sequence.
To troubleshoot these issues, you can try the following:
- Review your filter settings and check for any errors or conflicts.
- Verify that your filters are accurately reflecting the data you want to include or exclude.
- Check for missing data and adjust your filters accordingly.
- Experiment with different filter configurations to see if this resolves the issue.
- Remove filters to see if this improves the accuracy of your data.
- Consult Google Analytics documentation or seek help from support forums or experts.
Case examples of views with filters in Google Analytics
here are a few case examples of views with filters in Google Analytics:
- Exclude Internal Traffic: One of the most common use cases for views with filters in Google Analytics is to exclude internal traffic from analytics reports. This helps ensure that your reports accurately reflect external user behavior, without being skewed by internal traffic from employees or partners. To set up this filter, create a new view and apply an IP address filter to exclude traffic from your office or other internal locations.
- Filter by Geography: If you have a global audience, you might want to set up views with filters to track user behavior by geographic region. This can help you identify trends and opportunities for targeting specific regions with your marketing and advertising efforts. To set up this filter, create a new view and apply a geographic filter to include or exclude traffic from specific countries or regions.
- Exclude Bots and Spammers: Another common use case for views with filters is to exclude bot and spam traffic from analytics reports. This can help ensure that your reports accurately reflect real user behavior, without being skewed by automated or malicious traffic. To set up this filter, create a new view and apply a filter to exclude traffic from known bot and spam IP addresses.
- Filter by Device Type: If you have a mobile app or responsive website, you might want to set up views with filters to track user behavior by device type. This can help you identify trends and opportunities for optimizing your user experience for specific devices. To set up this filter, create a new view and apply a device type filter to include or exclude traffic from specific devices or operating systems.
- Filter by Traffic Source: Finally, you might want to set up views with filters to track user behavior by traffic source. This can help you identify which channels are driving the most traffic and engagement, and adjust your marketing and advertising strategies accordingly. To set up this filter, create a new view and apply a traffic source filter to include or exclude traffic from specific sources, such as social media or paid search.
FAQs about Filters in Google Analytics
What is the filter limit in Google Analytics?
Answer: Google Analytics allows you to create up to 10 data filters per property. However, it is important to note that filters can impact your data permanently, so it is recommended to test them on a small subset of data before applying them to your entire view.
What data filtering options do you have in Google Analytics?
Answer: Google Analytics offers several data filtering options, including include/exclude filters, search and replace filters, lowercase/uppercase filters, and advanced filters that allow you to create custom filter patterns. These filters can help you refine your data and get more accurate insights into your website’s performance.
Overall, Google Analytics Filters offer an efficient and invaluable tool for managing and analyzing data from your website. With the help of these filters, you can customize your data sets so that you’re able to get more targeted insights about your visitors and track their behaviors. Through careful application, customization and organization of your filters, you will be able to maintain a comprehensive view of who visits your website and why. Working with Filters in Google Analytics can be tricky at first, but with time and practice, it won’t be long before you become an expert in leveraging them to maximize the data-driven decisions and results on your website.



0 responses on "Complete Guide To Google Analytics Filters"